
Apr 6, 2024

In the realm of process industries, understanding pressure measurement is paramount for ensuring optimal performance and safety. Pressure, the force exerted per unit area, is a fundamental parameter that directly influences various industrial processes. Let’s delve into the basics of pressure measurement, with a specific focus on pressure gauges, and essential tools for monitoring pressure levels in industrial environments.
Pressure measurement serves as a vital indicator of process conditions, aiding in the control and regulation of operations. Whether it’s monitoring fluid flow in pipelines, assessing vessel integrity, or optimizing equipment performance, accurate pressure measurement is indispensable.
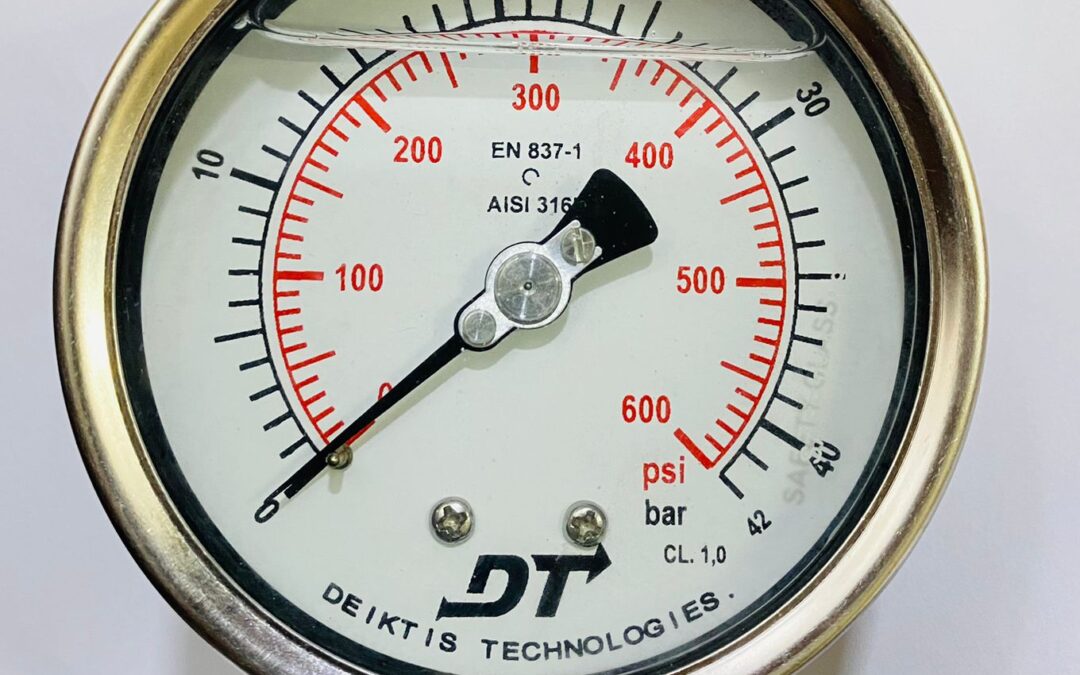
Pressure gauges are instrumental devices utilized for measuring and displaying pressure levels within industrial systems. These gauges come in a variety of types, including Bourdon tube gauges, diaphragm gauges, and digital pressure gauges, each tailored to specific applications and pressure ranges.
Bourdon tube gauges, the most common type, operate on the principle of elastic deformation. When pressure is applied, the curved tube within the gauge straightens slightly, causing a pointer to move along a calibrated scale, indicating pressure readings.
Diaphragm gauges employ a flexible diaphragm that deflects in response to pressure changes, translating the deflection into pressure readings. These gauges are suitable for measuring low pressures and are often used in applications requiring high accuracy.
Digital pressure gauges, on the other hand, utilize electronic sensors to measure pressure and display readings digitally. These gauges offer advantages such as precise measurements, remote monitoring capabilities, and compatibility with digital communication protocols.
Regardless of the type, pressure gauges require proper installation, calibration, and maintenance to ensure accuracy and reliability. Regular calibration against known standards is essential to verify gauge accuracy and correct any deviations.
In conclusion, pressure measurement is a fundamental aspect of process industries, enabling effective monitoring and control of industrial processes. Pressure gauges play a pivotal role in this regard, providing real-time insights into pressure conditions within industrial systems. Understanding the basics of pressure measurement and selecting the appropriate gauge for each application is crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring operational safety in process industries.
Mar 30, 2024

Introduction:
Welcome to DeiktisTech, where we delve into the intricacies of industrial processes and technologies. In this inaugural blog post, we embark on a journey to demystify the realm of process measurement in industries. From manufacturing plants to chemical refineries, process measurement plays a pivotal role in ensuring efficiency, quality, and safety. Let’s unravel the fundamentals and significance of process measurement, shedding light on its importance and various methodologies employed across industries.
Understanding Process Measurement:
At its core, process measurement involves quantifying and analyzing various parameters within industrial processes to monitor, control, and optimize operations. These parameters could range from temperature, pressure, flow rates, to chemical compositions and more, depending on the specific requirements of each process. The precise measurement of these variables enables industries to maintain optimal conditions, ensure product quality, and enhance overall productivity.
Importance of Process Measurement:
The importance of process measurement cannot be overstated in the realm of industries. It serves as the eyes and ears of process control systems, providing real-time data essential for decision-making and troubleshooting. Whether it’s maintaining tight tolerances in manufacturing processes or adhering to stringent environmental regulations, accurate measurement forms the foundation of operational excellence and regulatory compliance.
Key Components of Process Measurement:
Process measurement systems typically comprise several key components:
- Sensors and Instruments: These are the frontline components responsible for capturing data from the process environment. Sensors come in various forms, including temperature sensors, pressure transmitters, level detectors, and analytical instruments tailored to specific applications.
- Data Acquisition Systems: Once data is collected from sensors, it needs to be processed and transmitted for analysis. Data acquisition systems play a crucial role in converting analog signals from sensors into digital data, which can be further processed by control systems or displayed for operators.
- Control Systems: In many industrial processes, measurement data is not only collected but also utilized for real-time control and automation. Control systems integrate measurement data with control algorithms to regulate process parameters and ensure optimal performance.
- Calibration and Maintenance: Regular calibration and maintenance of measurement instruments are essential to uphold accuracy and reliability. Calibration procedures ensure that instruments provide accurate readings, while proactive maintenance minimizes downtime and ensures uninterrupted operations.
Methodologies in Process Measurement:
Various methodologies are employed in process measurement, ranging from traditional techniques to cutting-edge technologies. These include:
- Direct Measurement: Direct measurement involves physically sensing and quantifying process parameters using sensors and instruments.
- Indirect Measurement: In some cases, process parameters are inferred or indirectly measured based on related variables or properties.
- Non-contact Measurement: Non-contact measurement techniques, such as infrared thermography or ultrasonic sensing, are utilized to measure parameters without physical contact with the process.
Conclusion: In conclusion, process measurement forms the backbone of modern industrial operations, enabling precise monitoring, control, and optimization of processes across diverse sectors. By understanding the fundamentals and significance of process measurement, industries can unlock new avenues for efficiency improvement, quality enhancement, and sustainable growth. Stay tuned as we delve deeper into the intricacies of process measurement in upcoming posts, exploring advanced techniques, case studies, and emerging trends in this dynamic field.
Join us at DeiktisTechnologies (DT) as we continue to unravel the complexities of industrial processes and technologies, empowering industries to thrive in an ever-evolving landscape.




